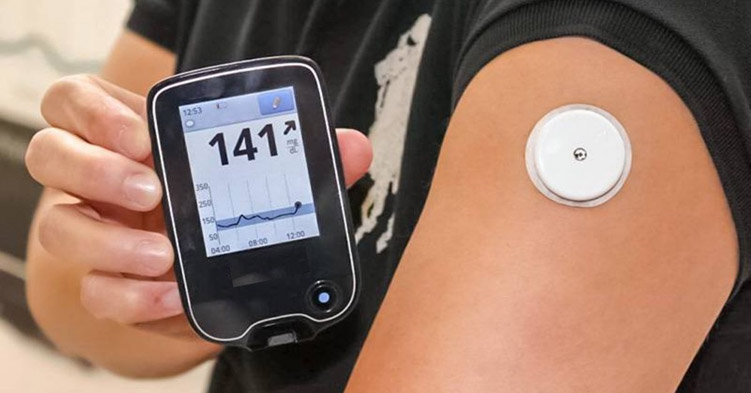
NALAM's CGMS
Long term diabetic complications can be prevented or reduced by achieving good metabolic control, reflected by HbA1c. To reach good glycemic control, frequent self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) must be performed.
SMBG devices provide the patient with accurate but discrete blood glucose levels. However, they do not provide trend information, nor do they reflect glycemic fluctuations. This is possible by using Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems.
Compared with a standard blood glucose meter, using a CGM system can help you
- better manage your glucose levels every day
- have fewer low blood glucose emergencies
- need fewer finger sticks
A graphic on the CGM screen shows whether your glucose is rising or dropping—and how quickly—so you can choose the best way to reach your target glucose level. Over time, good management of glucose greatly helps people with diabetes stay healthy and prevent complications of the disease.
The CGM systems display the glucose level, the direction and magnitude of change of glucose levels, and can be used as a tool to predict impending glucose excursions (hypo- and hyperglycemia), and to assess glycemic variability. In addition, reliable alarm signals of low or high glucose values warn the patient to take action. All this is being executed on a near-continuous basis, throughout the day, and this for several days, thereby facilitating pattern recognition, and helping the patient and physician to optimize therapy and improve metabolic control.
Real-time CGM systems represents a major advantage for the diabetic patient with hypoglycemia unawareness, allowing the patient to feel more confident and to improve metabolic control and quality of life.